
What is sebaceous cyst, its major symptoms and top 5 effective treatment measures?
What is a sebaceous cyst?
A slow-growing cyst that develops straight from the sebaceous glands. Keratin cysts, epidermal cysts, and epithelial cysts are other names for them. They affect approximately 20% of adults and they typically don't show signs like pain or discomfort and are non cancerous in nature.
Though, slow growing bumps under the skin may occasionally develop an infection, become inflammatory, or even rupture. Such cysts might require medical attention.

Types of sebaceous cysts
Epidermoid Cyst
Characteristics:
- Grows slowly
- Vary in size
- Not painful
- Filled with dead skin cells
- Might have sebaceous cyst punctum or tiny hole in center
- Tender if infected
- Drains grayish, sometimes smelly
Pilar Cyst
Characteristics:
- Forms from hair follicle
- Firm, Round, Smooth
- Filled with cytokeratin
- Does not have punctum
- Most commonly found on scalp
Where do sebaceous cysts come from?
You must comprehend the functions of sebaceous glands in order to comprehend how sebaceous cysts develop. These glands, which are found beneath the skin, release oil known as sebum. The skin and hair are coated by this oil. The majority of sebaceous glands are found around hair follicles, while some are also found on the skin's exposed surface.

The duct, or a tube by which the oil from these glands leaves the skin, can occasionally become harmed and obstructed. Any cause, such as a scrape, surgical wound, or even acne, might cause the blockage. The cyst frequently becomes apparent in days weeks or even months after it has grown because of how slowly it grows.
The fluid, or sebum, escapes from the cyst as you squeeze it. Despite being generally benign, a cyst will turn red and begin to enlarge if it becomes infected. There is a chance that sebaceous cyst causes bad-smelling secretion.It is advised to visit a doctor and contact them if these symptoms are present.
How to recognise an infected sebaceous cyst?
The initial size of these sebaceous cysts is typically tiny when they are first discovered. They are small, rounded, occasionally slightly reddish from the top, and typically not unpleasant. If ignored, it might enlarge and become uncomfortable.

Sebaceous cysts occur on the neck and face and may cause pressure and unusual pain.. Because they contain semi-liquid keratin, they are frequently velvety to the touch. These are frequently noted to be non-cancerous, and their growth progresses slowly. However, occasionally these cysts may develop exceptionally quickly and contain cancerous cells. When removed, a malignant sebaceous cyst may quickly grow again in the same or a different location, exhibit unusual redness, a yellowish discharge, and can be painful. They also have a diameter greater than 5 cm.
How are sebaceous cysts treated?
Sebaceous cysts could be disregarded if they are small, not unpleasant, and not expanding because they are typically not hazardous. Your healthcare practitioner may inject a steroid medication into a tiny cyst if it gets inflammatory to lessen swelling. A big, sensitive, or irritated cyst may be drained by a medical professional. If larger cysts interfere with clothing or cause baldness on the scalp, they may need to be removed.

There are number of processes your doctor can use for sebaceous cyst removal surgically:
Medication
In order to treat infectious sebaceous cysts, dermatologists may give antibiotics as pills, topical creams, or injectables. These will lessen the cysts' pain and swelling.
Surgery
Dermatologists use a crochet needle or scalpel to remove your cyst when the swelling subsides and the area has been sanitised. They might also stitch the wound. After this operation, cysts often do not reoccur if they are entirely removed together with their wall.the surgrical method involves following steps:
Sterilisation: To minimise the risk of infection, the region to be treated is prepped by sanitising the adjoining skin with just an antiseptic (povidone-iodine) solution.
Anaesthesia: To lessen or eliminate pain during the procedure, a local anaesthetic (2% lignocaine plus adrenaline) is administered or topically to the location.
Removal: One of the most necessary part of sebaceous cyst treatment is the cyst removal which is done by making a small opening in the cyst's core (punctum) with a blade or radiofrequency, the cyst's contents are released through that opening, the cyst wall is removed, and the opening is then repaired with sutures (surgical threads) if necessary and dressed.
Incision and drainage (I&D):
In cases where the cyst has an infection due to pus collection, this procedure is performed. Symptomatic relief and pus drainage are the only purposes of this procedure. Further cysts can be removed surgically once the infection subsides.
Excision:
In this type of treatment cyst is entirely eliminated by punch excision or surgical excision and is possible for very tiny lesions.
Note: Never attempt to rupture and drain a cyst on your own. By doing so, an infection can spread and the cyst might re-grow. Also popping sebaceous cyst with your finger nails is also a bad idea as the infection spreads resulting in overgrowth of the lesion.
Non surgical treatments

Hot compress
The most suggested and efficient at-home treatment for cyst draining or cyst shrinkage is simple heat. Heat may cause the cyst's fluids to thin out. This may speed up the process of fluid drainage further into lymphatic systems that are liquid-filled. This system participates in the body's fluid balance maintenance and infection defence.
Aloe Vera
Studies have proved that Aloe Vera is an excellent anti-inflammatory and microbicidal agent. Both could be beneficial for cyst pain and inflammation. Aloe Vera also may aid in reducing or eliminating certain cysts brought on by pathogens or other infections. You can either massage natural aloe leaf or aloe Vera gel gently near the infected area.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree essential oil may, aid in curing cysts either directly or indirectly. However, tea tree oil exerts remarkable antibacterial properties with an activity against inflammation. This means that while it is less potent and effective than synthetic substances, it still destroys bacteria, viruses, fungus, and other pathogens.
Ingrown hairs can lead to cysts in some cases. These develop when sebaceous gland infection results from improper hair follicle growth. As a result, a pus pocket is formed that may develop into a sebaceous cyst.
Antibacterial properties may assist in combating bacterial infections brought on by ingrown hairs. It might lessen the likelihood of developing an ingrown hair cyst or lessen the severity of the cyst itself.
What else to do?

- Stop popping sebaceous cyst
- Keep it clean and dry
- Using ice for inflammation
When Should a Cyst Be Removed?
It is usually not necessary to remove a harmless cyst unless it is causing pain, discomfort, or affecting selfconfidence.The same logic is true whether you decide to get treatment for acne or not. Additionally, acne medications can frequently clear your skin of cystic acne without you having to surgically remove any cysts. If the type of cyst you see on your body has cancerous tissue or is infected, it needs to be medically reviewed and removed. To prevent further issues, it is frequently imperative in these situations to treat skin cysts as soon as feasible. Except in extreme circumstances, cyst removal is rarely necessary unless you are having problems with it.
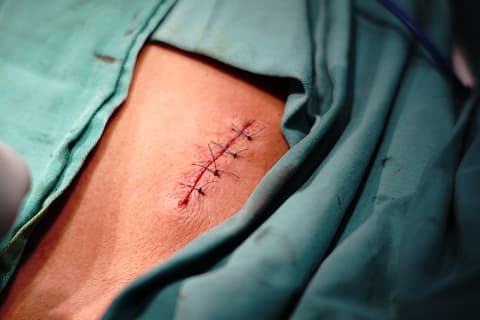
Take away
There is a possibility of sebaceous cysts developing on your skin, especially on the face, neck, and other areas where the sebaceous glands are obstructed or ruptured. In most cases, they don't spread disease or start malignancy. They disappear on their own but when they develop inflammation, infection, or sensitivity, surgical methods are indicated. Avoid squeezing them and make sure you keep them clean to prevent the illness from spreading. If it burns or hurts and lasts for a while, then see a doctor or your family physician as soon as possible.
FAQs
Q. What might occur if sebaceous cysts are not promptly treated?
Even if the cyst is not diseased, it may become sore or bloated. A hard surface will almost certainly rub against the cyst, which could break open and lead to an infection. A painful abscess may develop inside the cyst as well. If the cyst accumulates too much pus or liquid, it could explode on its own or resemble a boil. As a result, the cyst's fluids will flow out and infect the skin around them. Rarely, the cyst may become malignancy and disseminate the infection to nearby healthy tissues.
Q. What negative effects might surgery for sebaceous cysts cause?
- Anesthesia-related reactions,
- Excessive bleeding throughout the operation
- Blood clot development
- Damage to the nearby structures
- Sense of numbness or tingling there
- Bruising or swelling at the site of the operation
- Late scarring and delayed healing
- Contamination of the wound
- Recurring cyst
